[ad_1]
PageRank (PR) is a Google algorithm that ranks net pages in search outcomes by evaluating the quantity and high quality of hyperlinks to a web page. It operates on the precept that pages receiving extra high-quality hyperlinks are deemed extra essential and are thus ranked greater.
PageRank was created by Google co-founders Sergey Brin and Larry Web page in 1997 after they have been at Stanford College, and the identify is a reference to each Larry Web page and the time period “webpage.”
In some ways, it’s just like a metric known as “impression issue” for journals, the place extra cited = extra essential. It differs a bit in that PageRank considers some votes extra essential than others.
Through the use of hyperlinks together with content material to rank pages, Google’s outcomes have been higher than opponents. Hyperlinks grew to become the forex of the net.
Need to know extra about PageRank? Let’s dive in.
By way of fashionable search engine optimisation, PageRank is among the algorithms comprising Experience Expertise Authoritativeness Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T).
Google’s algorithms determine indicators about pages that correlate with trustworthiness and authoritativeness. The most effective identified of those indicators is PageRank, which makes use of hyperlinks on the net to grasp authoritativeness.
Supply: How Google Fights Disinformation
We’ve additionally had affirmation from Google reps like Gary Illyes, who stated that Google nonetheless makes use of PageRank and that hyperlinks are used for E-A-T (now E-E-A-T).
https://twitter.com/methode/standing/829755916895535104
https://twitter.com/patrickstox/standing/974318705633935360
After I ran a study to measure the impact of links and successfully eliminated the hyperlinks utilizing the disavow software, the drop was apparent. Hyperlinks nonetheless matter for rankings.
PageRank has additionally been a confirmed issue in relation to crawl budget. It is smart that Google needs to crawl essential pages extra typically.
PageRank can also be a canonicalization signal. Pages with a better PageRank usually tend to be chosen because the canonical model that will get listed and proven to customers.
Loopy truth: The method revealed within the unique PageRank paper was flawed. Let’s have a look at why.
PageRank was described in the original paper as a chance distribution—or how doubtless you have been to be on any given web page on the net. Because of this when you sum up the PageRank for each web page on the net collectively, it’s best to get a complete of 1.
Right here’s the complete PageRank method from the unique paper revealed in 1997:
PR(A) = (1-d) + d (PR(T1)/C(T1) + … + PR(Tn)/C(Tn))
Simplified a bit and assuming the damping issue (d) is 0.85 as Google talked about within the paper (I’ll clarify what the damping issue is shortly), it’s:
PageRank for a web page = 0.15 + 0.85 (a portion of the PageRank of every linking web page cut up throughout its outbound hyperlinks)
Within the paper, they stated that the sum of the PageRank for each web page ought to equal 1. However that’s not doable when you use the method within the paper. Every web page would have a minimal PageRank of 0.15 (1-d). Just some pages would put the overall at larger than 1. You may’t have a chance larger than 100%. One thing is flawed!
The method ought to truly divide that (1-d) by the variety of pages on the web for it to work as described. It will be:
PageRank for a web page = (0.15/variety of pages on the web) + 0.85 (a portion of the PageRank of every linking web page cut up throughout its outbound hyperlinks)
It’s nonetheless difficult, so let’s see if I can clarify it with some visuals.
1. A web page is given an preliminary PageRank rating primarily based on the hyperlinks pointing to it. Let’s say I’ve 5 pages with no hyperlinks. Every will get a PageRank of (1/5) or 0.2.
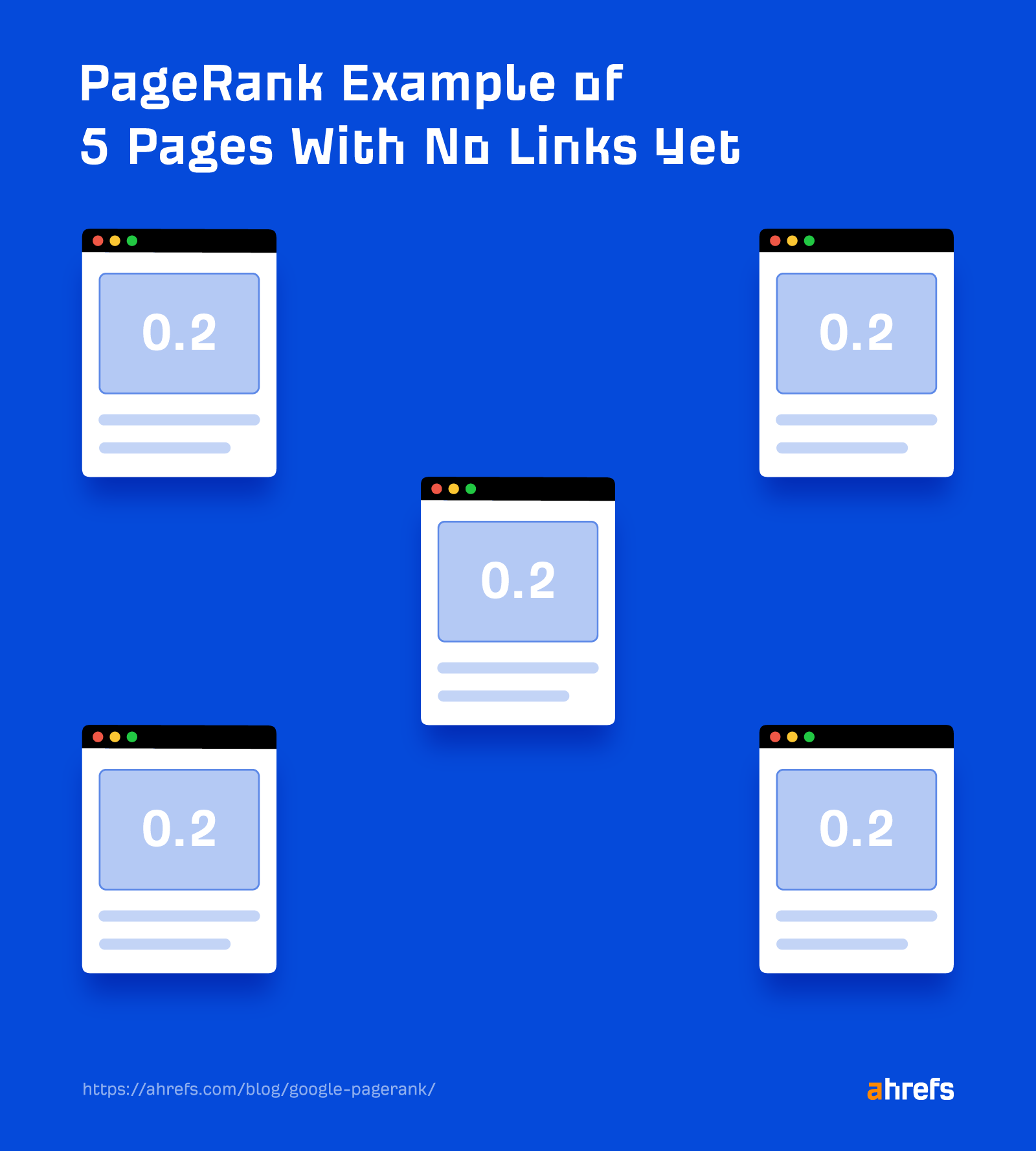
2. This rating is then distributed to different pages by the hyperlinks on the web page. If I add some hyperlinks to the 5 pages above and calculate the brand new PageRank for every, then I find yourself with this:
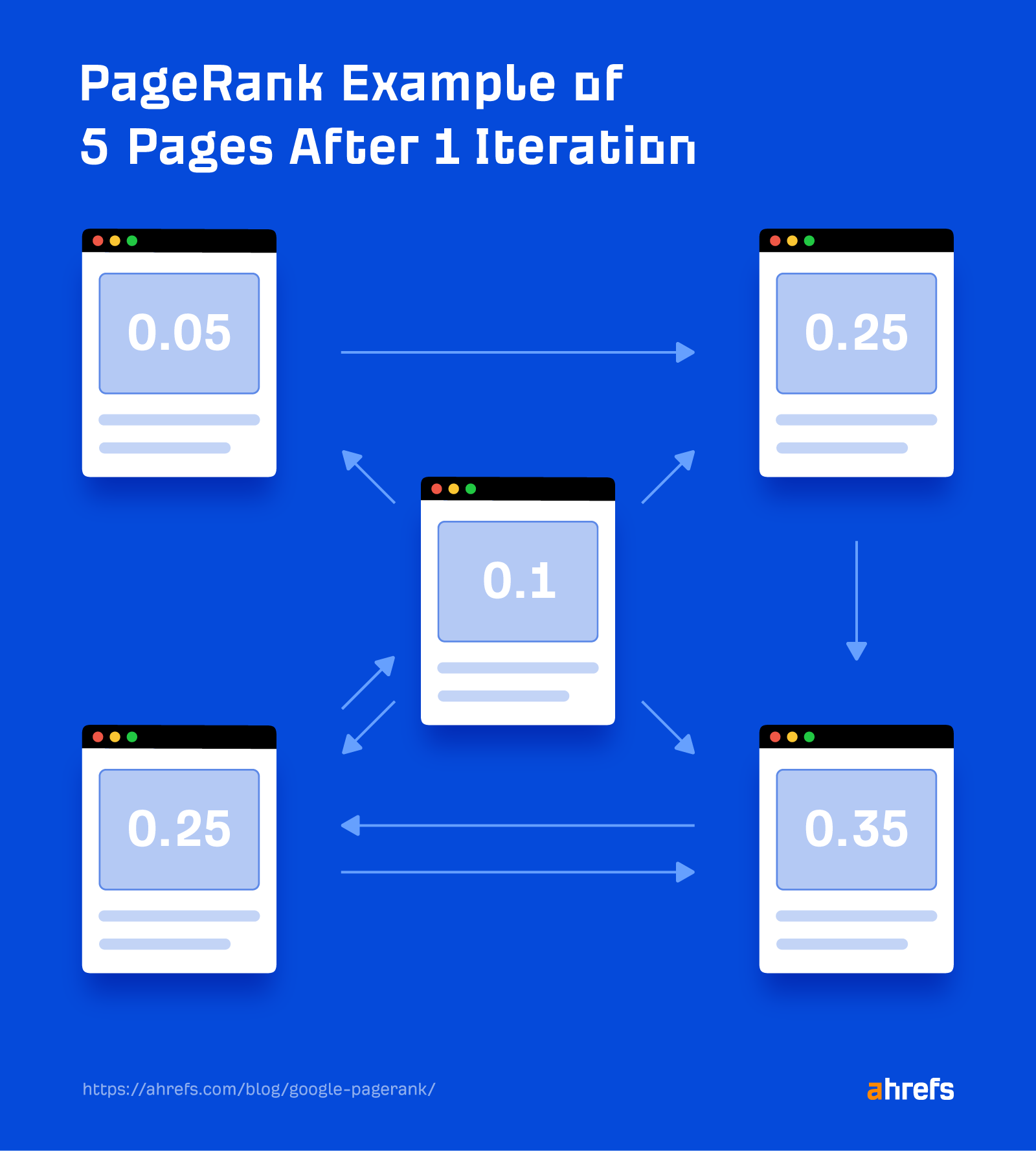
You’ll discover that the scores are favoring the pages with extra hyperlinks to them.
3. This calculation is repeated as Google crawls the net. If I calculate the PageRank once more (known as an iteration), you’ll see that the scores change. It’s the identical pages with the identical hyperlinks, however the base PageRank for every web page has modified, so the ensuing PageRank is completely different.
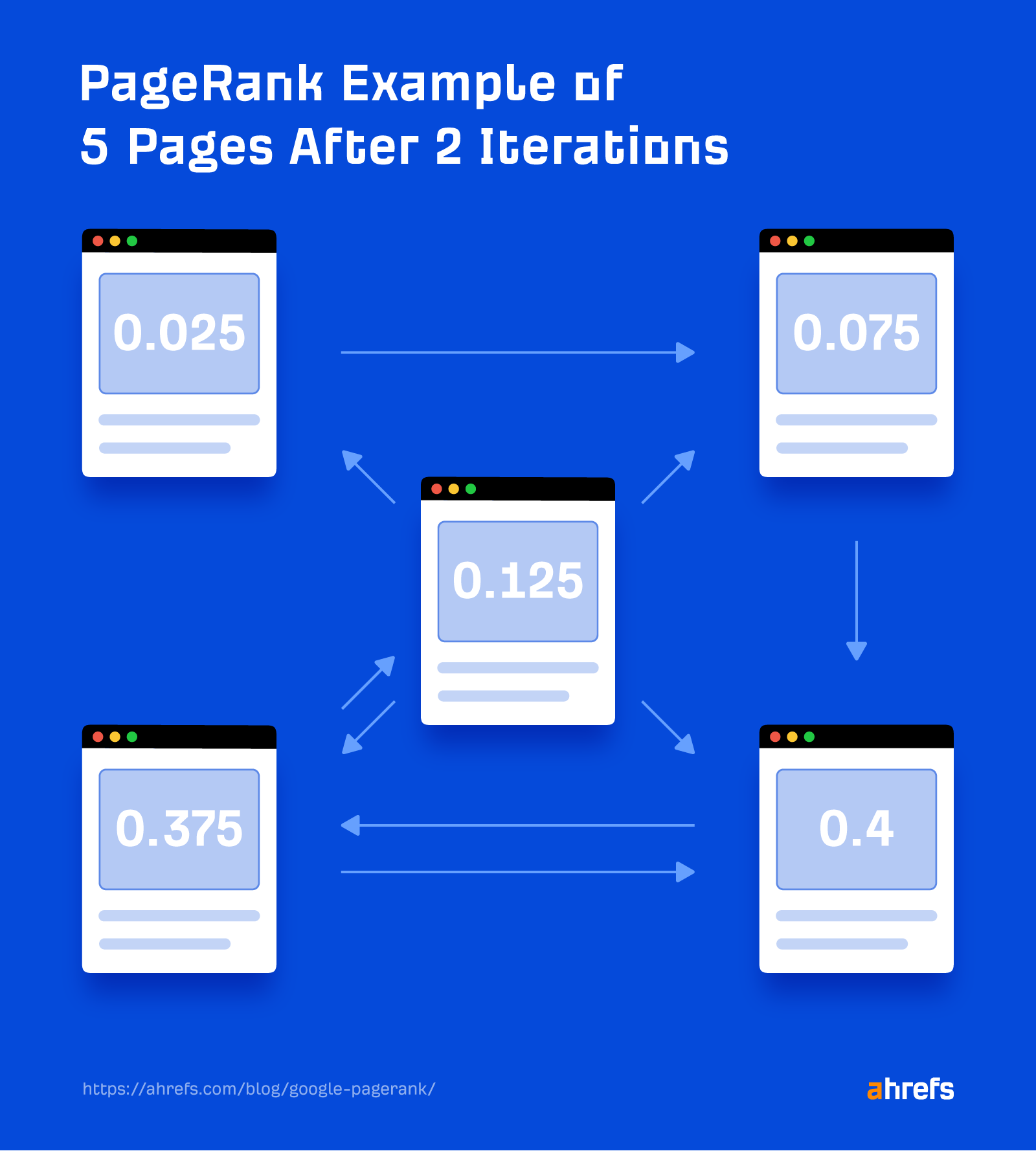
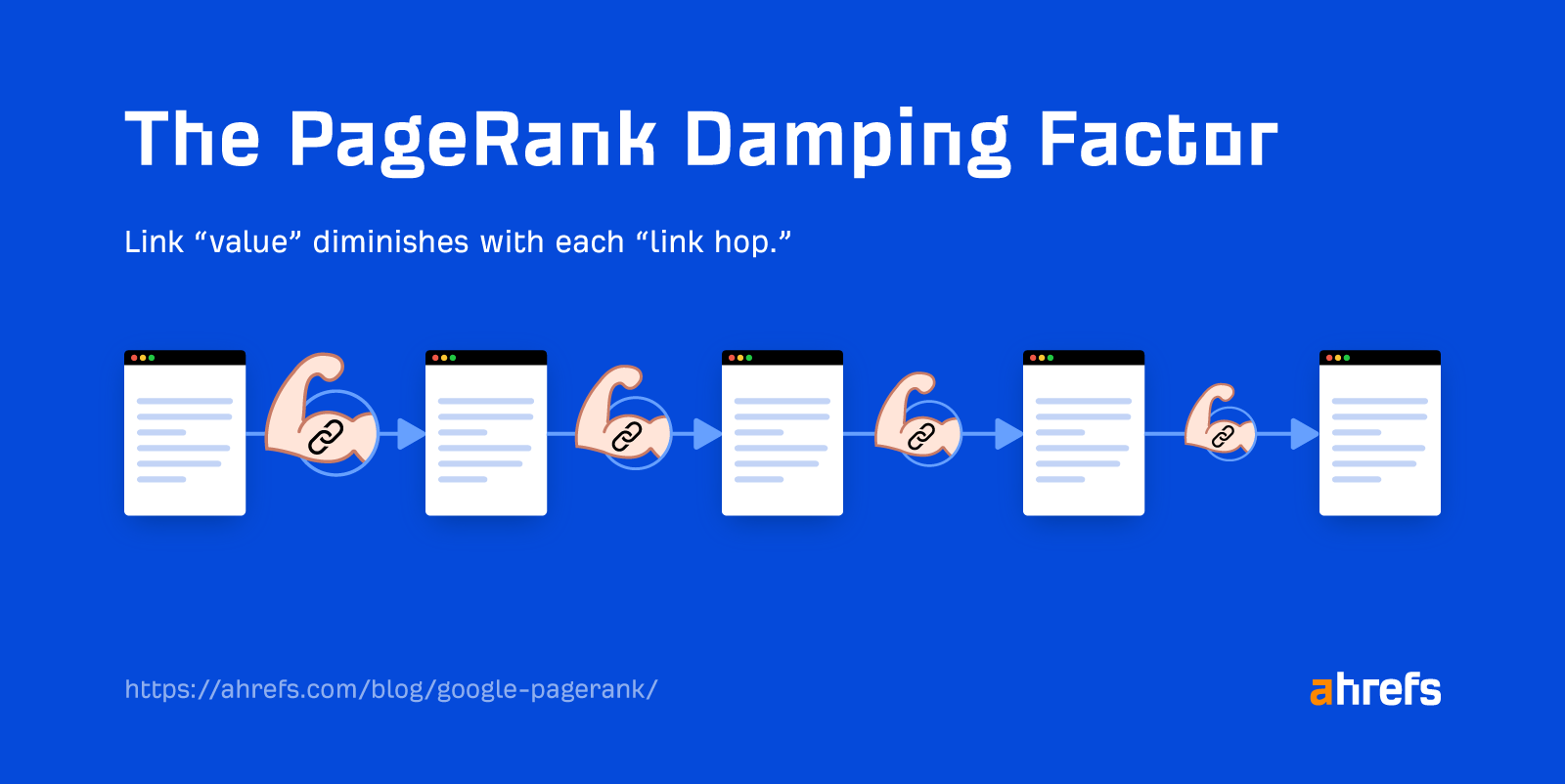
The PageRank method additionally has a so-called “damping issue,” the “d” within the method, which simulates the chance of a random person persevering with to click on on hyperlinks as they browse the net.
Consider it like this: The chance of you clicking a hyperlink on the primary web page you go to within reason excessive. However the chance of you then clicking a hyperlink on the following web page is barely decrease, and so forth and so forth.
If a robust web page hyperlinks instantly to a different web page, it’s going to cross loads of worth. If the hyperlink is 4 clicks away, the worth transferred from that sturdy web page might be so much much less due to the damping issue.
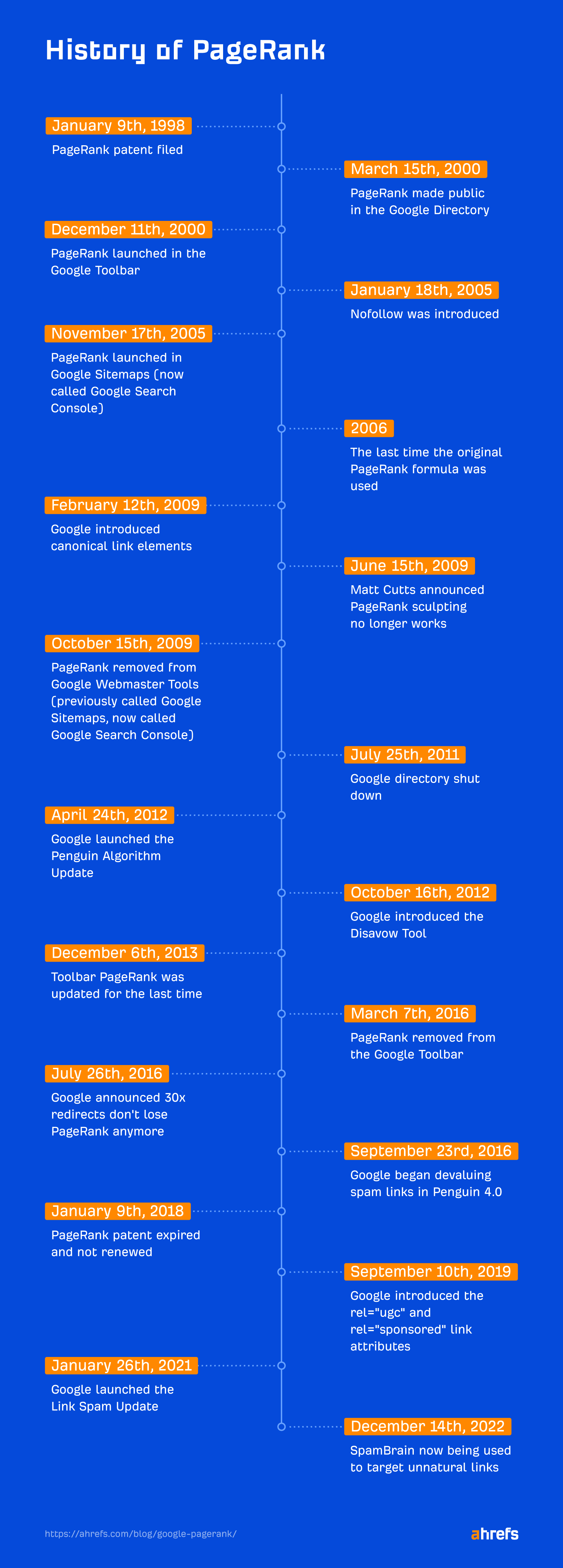
The primary PageRank patent was filed on January 9, 1998. It was titled “Method for node ranking in a linked database.” This patent expired on January 9, 2018, and was not renewed.
Google first made PageRank public when the Google Directory launched on March 15, 2000. This was a model of the Open Listing Undertaking however sorted by PageRank. The listing was shut down on July 25, 2011.
It was December 11, 2000, when Google launched PageRank in the Google toolbar, which was the model most SEOs obsessed over.
That is the way it seemed when PageRank was included in Google’s toolbar.
PageRank within the toolbar was final up to date on December 6, 2013, and was lastly eliminated on March 7, 2016.
The PageRank proven within the toolbar was a bit completely different. It used a easy 0–10 numbering system to symbolize the PageRank. However PageRank itself is a logarithmic scale the place reaching every greater quantity turns into more and more troublesome.
PageRank even made its way into Google Sitemaps (now referred to as Google Search Console) on November 17, 2005. It was proven in classes of excessive, medium, low, or N/A. This function was eliminated on October 15, 2009.
Hyperlink spam
Through the years, there have been loads of alternative ways SEOs have abused the system within the seek for extra PageRank and higher rankings. Google has an entire list of link schemes that embody:
- Shopping for or promoting hyperlinks—exchanging hyperlinks for cash, items, merchandise, or providers.
- Extreme hyperlink exchanges.
- Utilizing software program to routinely create hyperlinks.
- Requiring hyperlinks as a part of a phrases of service, contract, or different settlement.
- Textual content advertisements that don’t use nofollow or sponsored attributes.
- Advertorials or native promoting that features hyperlinks that cross rating credit score.
- Articles, visitor posts, or blogs with optimized anchor textual content hyperlinks.
- Low-quality directories or social bookmark hyperlinks.
- Key phrase-rich, hidden, or low-quality hyperlinks embedded in widgets that get placed on different web sites.
- Extensively distributed hyperlinks in footers or templates. For instance, hard-coding a hyperlink to your web site into the WP Theme that you simply promote or give away for free.
- Discussion board feedback with optimized hyperlinks within the put up or signature.
The techniques to fight hyperlink spam have advanced through the years. Let’s have a look at a number of the main updates.
Nofollow
On January 18, 2005, Google introduced it had partnered with different main search engines like google and yahoo to introduce the rel=“nofollow” attribute. It inspired customers so as to add the nofollow attribute to weblog feedback, trackbacks, and referrer lists to assist fight spam.
Right here’s an excerpt from Google’s official assertion on the introduction of nofollow:
In case you’re a blogger (or a weblog reader), you’re painfully aware of individuals who attempt to increase their very own web sites’ search engine rankings by submitting linked weblog feedback like “Go to my low cost prescription drugs web site.” That is known as remark spam, we don’t prefer it both, and we’ve been testing a brand new tag that blocks it. To any extent further, when Google sees the attribute (rel=“nofollow”) on hyperlinks, these hyperlinks received’t get any credit score after we rank web sites in our search outcomes.
Nearly all fashionable techniques use the nofollow attribute on weblog remark hyperlinks.
SEOs even started to abuse nofollow—due to course we did. Nofollow was used for PageRank sculpting, the place individuals would nofollow some hyperlinks on their pages to make different hyperlinks stronger. Google finally modified the system to forestall this abuse.
In 2009, Google’s Matt Cutts confirmed that this may now not work and that PageRank could be distributed throughout hyperlinks even when a nofollow attribute was current (however solely handed by the adopted hyperlink).
Google added a couple more link attributes which might be extra particular variations of the nofollow attribute on September 10, 2019. These included rel=“ugc” meant to determine user-generated content material and rel=“sponsored” meant to determine hyperlinks that have been paid or affiliate.
Algorithms concentrating on hyperlink spam
As SEOs discovered new methods to sport hyperlinks, Google labored on new algorithms to detect this spam.
When the unique Penguin algorithm launched on April 24, 2012, it damage loads of web sites and web site homeowners. Google gave web site homeowners a solution to get well later that 12 months by introducing the disavow tool on October 16, 2012.
When Penguin 4.0 launched on September 23, 2016, it introduced a welcome change to how hyperlink spam was dealt with by Google. As a substitute of injuring web sites, it started devaluing spam hyperlinks. This additionally meant that almost all websites now not wanted to make use of the disavow software.
Google launched its first Link Spam Update on July 26, 2021. This just lately advanced, and a Link Spam Update on December 14, 2022, introduced using an AI-based detection system known as SpamBrain to neutralize the worth of unnatural hyperlinks.
The unique model of PageRank hasn’t been used since 2006, in keeping with a former Google worker. The worker stated it was changed with one other much less resource-intensive algorithm.
They changed it in 2006 with an algorithm that offers approximately-similar outcomes however is considerably sooner to compute. The substitute algorithm is the quantity that’s been reported within the toolbar, and what Google claims as PageRank (it even has the same identify, and so Google’s declare isn’t technically incorrect). Each algorithms are O(N log N) however the substitute has a a lot smaller fixed on the log N issue, as a result of it does away with the necessity to iterate till the algorithm converges. That’s pretty essential as the net grew from ~1-10M pages to 150B+.
Keep in mind these iterations and the way PageRank stored altering with every iteration? It appears like Google simplified that system.
What else has modified?
Some hyperlinks are value greater than others
Reasonably than splitting the PageRank equally between all hyperlinks on a web page, some links are valued more than others. There’s hypothesis from patents that Google switched from a random surfer mannequin (the place a person might go to any hyperlink) to a reasonable surfer model (the place some hyperlinks usually tend to be clicked than others so that they carry extra weight).
Some hyperlinks are ignored
There have been a number of techniques put in place to disregard the worth of sure hyperlinks. We’ve already talked about a number of of them, together with:
- Nofollow, UGC, and sponsored attributes.
- Google’s Penguin algorithm.
- The disavow software.
- Hyperlink Spam updates.
Google additionally received’t rely any hyperlinks on pages which might be blocked by robots.txt. It received’t be capable of crawl these pages to see any of the hyperlinks. This method was doubtless in place from the begin.
Some hyperlinks are consolidated
Google has a canonicalization system that helps it decide what model of a web page needs to be listed and to consolidate indicators from duplicate pages to that important model.
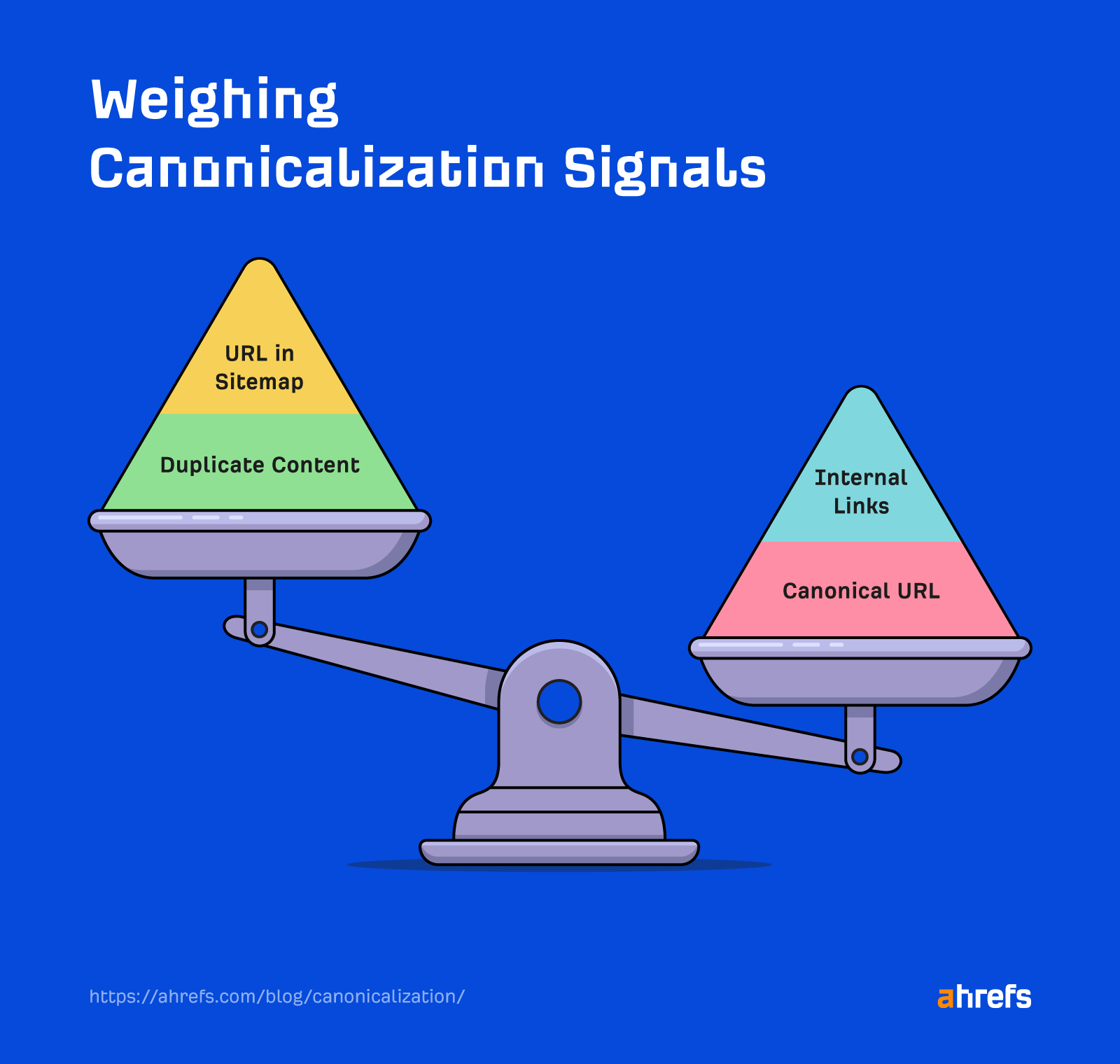
Canonical link elements have been launched on February 12, 2009, and permit customers to specify their most popular model.
Redirects have been initially stated to cross the identical quantity of PageRank as a hyperlink. However in some unspecified time in the future, this method modified and no PageRank is at present misplaced.
https://twitter.com/methode/standing/757923179641839616
A bit continues to be unknown
When pages are marked as noindex, we don’t precisely understand how Google treats the hyperlinks. Even Googlers have conflicting statements.
Based on John Mueller, pages that are marked noindex will eventually be treated as noindex, nofollow. Because of this the hyperlinks finally cease passing any worth.
Based on Gary, Googlebot will discover and follow the links as long as a page still has links to it.
These aren’t essentially contradictory. However when you go by Gary’s assertion, it could possibly be a really very long time earlier than Google stops crawling and counting hyperlinks—maybe by no means.
There’s at present no solution to see Google’s PageRank.
URL Rating (UR) is an efficient substitute metric for PageRank as a result of it has so much in widespread with the PageRank method. It exhibits the power of a web page’s hyperlink profile on a 100-point scale. The larger the quantity, the stronger the hyperlink profile.
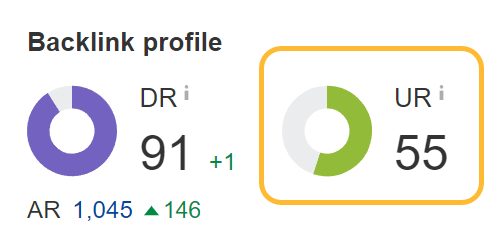
Each PageRank and UR account for inner and exterior hyperlinks when being calculated. Lots of the different power metrics used within the trade utterly ignore inner hyperlinks. I’d argue hyperlink builders needs to be trying extra at UR than metrics like DR, which solely accounts for hyperlinks from different websites.
Nonetheless, it’s not precisely the identical. UR does ignore the worth of some hyperlinks and doesn’t rely nofollow hyperlinks. We don’t know precisely what hyperlinks Google ignores and don’t know what hyperlinks customers might have disavowed, which can impression Google’s PageRank calculation. We additionally might make completely different selections on how we deal with a number of the canonicalization indicators like canonical hyperlink components and redirects.
So our recommendation is to make use of it however know that it might not be precisely like Google’s system.
We even have Page Rating (PR) in Site Audit’s Web page Explorer. That is just like an inner PageRank calculation and may be helpful to see what the strongest pages in your web site are primarily based in your inner hyperlink construction.
Since PageRank relies on hyperlinks, to extend your PageRank, you want higher hyperlinks. Let’s have a look at your choices.
Redirect damaged pages
Redirecting previous pages in your web site to related new pages can assist reclaim and consolidate indicators like PageRank. Web sites change over time, and folks don’t appear to love to implement correct redirects. This can be the simplest win, since these hyperlinks already level to you however at present don’t rely for you.
Right here’s methods to discover these alternatives:
I normally type this by “Referring domains.”
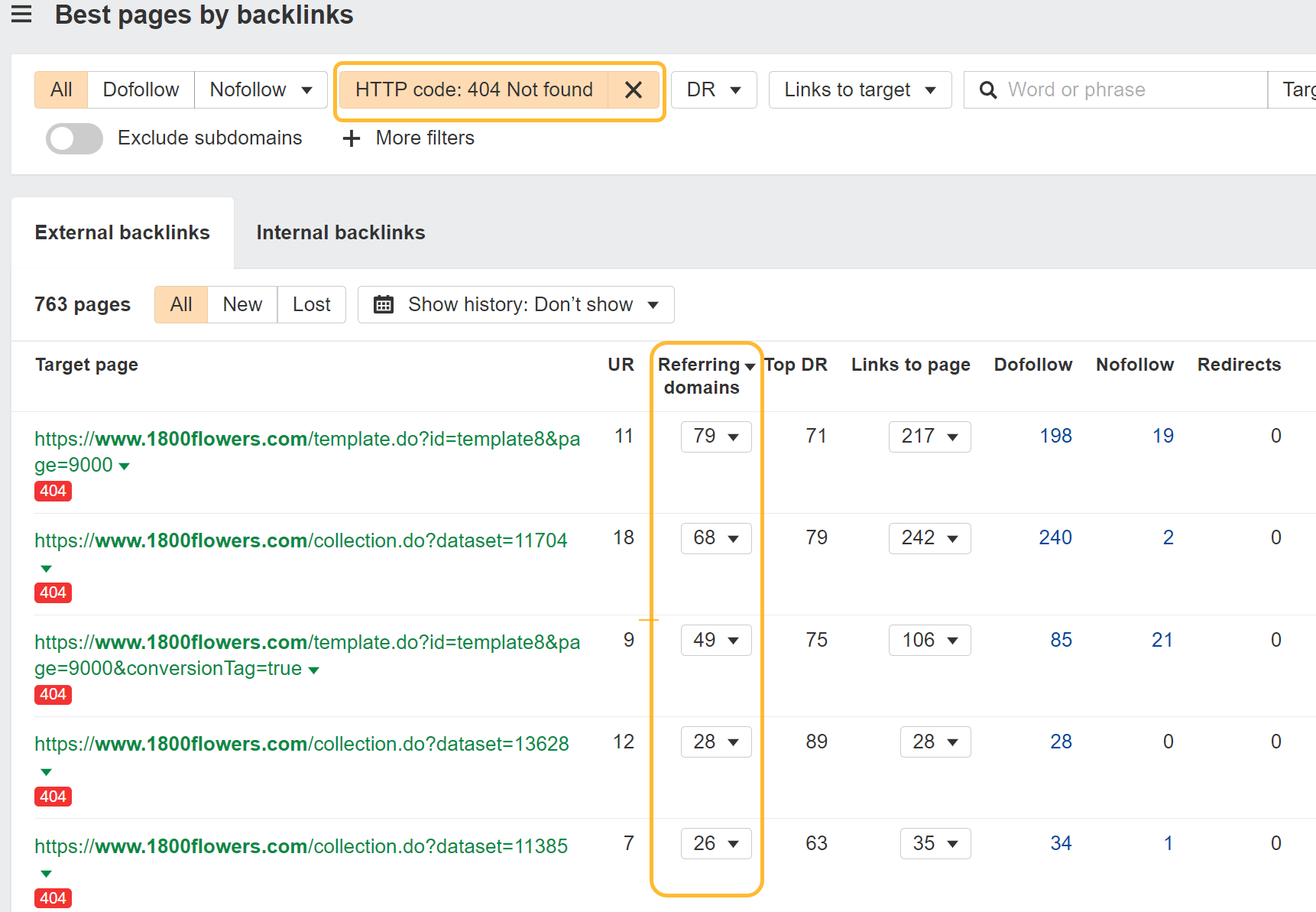
Take these pages and redirect them to the present pages in your web site. In case you don’t know precisely the place they go or don’t have the time, I’ve an automated redirect script that will assist. It appears on the previous content material from archive.org and matches it with the closest present content material in your web site. That is the place you doubtless need to redirect the pages.
Inner hyperlinks
Backlinks aren’t at all times inside your management. Folks can hyperlink to any web page in your web site they select, they usually can use no matter anchor textual content they like.
Inner hyperlinks are completely different. You will have full management over them.
Internally hyperlink the place it is smart. As an illustration, it’s possible you’ll need to hyperlink extra to pages which might be extra essential to you.
We’ve a software inside Site Audit known as Inner Hyperlink Alternatives that helps you shortly find these alternatives.
This software works by on the lookout for mentions of key phrases that you simply already rank for in your web site. Then it suggests them as contextual inner hyperlink alternatives.
For instance, the software exhibits a point out of “faceted navigation” in our information to duplicate content. As Website Audit is aware of now we have a web page about faceted navigation, it suggests we add an inner hyperlink to that web page.

Exterior hyperlinks
You may also get extra hyperlinks from different websites to your individual to extend your PageRank. We’ve loads of guides round hyperlink constructing already. A few of my favorites are:
Ultimate ideas
Though PageRank has modified, we all know that Google nonetheless makes use of it. We might not know all the main points or every part concerned, but it surely’s nonetheless straightforward to see the impression of hyperlinks.
Additionally, Google simply can’t appear to get away from utilizing hyperlinks and PageRank. It as soon as experimented with not utilizing hyperlinks in its algorithm and determined towards it.
So we don’t have a model like that that’s uncovered to the general public however now we have our personal experiments like that internally and the standard appears a lot a lot worse. It seems backlinks, though there’s some noise and definitely loads of spam, for essentially the most half are nonetheless a very actually huge win by way of high quality of search outcomes.
We performed round with the thought of turning off backlink relevance and a minimum of for now backlinks relevance nonetheless actually helps by way of ensuring that we flip the very best, most related, most topical set of search outcomes.
Supply: YouTube (Google Search Central)
When you’ve got any questions, message me on Twitter.
[ad_2]
Source link


