[ad_1]
Have fun the Holidays with a few of SEJ’s finest articles of 2023.
Our Festive Flashback sequence runs from December 21 – January 5, that includes every day reads on important occasions, fundamentals, actionable methods, and thought chief opinions.
2023 has been fairly eventful within the search engine marketing trade and our contributors produced some excellent articles to maintain tempo and replicate these adjustments.
Atone for the very best reads of 2023 to offer you lots to replicate on as you progress into 2024.
PageRank was as soon as on the very core of search – and was what made Google the empire it’s at this time.
Even when you imagine that search has moved on from PageRank, there’s no denying that it has lengthy been a pervasive idea within the trade.
Each search engine marketing professional ought to have grasp of what PageRank was – and what it nonetheless is at this time.
On this article, we’ll cowl:
- What’s PageRank?
- The historical past of how PageRank advanced.
- How PageRank revolutionized search.
- Toolbar PageRank vs. PageRank.
- How PageRank works.
- How PageRank flows between pages.
- Is PageRank nonetheless used?
Let’s dive in.
What Is PageRank?
Created by Google founders Larry Web page and Sergey Brin, PageRank is an algorithm based mostly on the mixed relative strengths of all of the hyperlinks on the Web.
Most individuals argue that the identify was based mostly on Larry Web page’s surname, while others counsel “Web page” refers to an internet web page. Each positions are doubtless true, and the overlap was in all probability intentional.
When Web page and Brin had been at Stanford College, they wrote a paper entitled: The PageRank Citation Ranking: Bringing Order to the Web.
Revealed in January 1999, the paper demonstrates a comparatively easy algorithm for evaluating the energy of net pages.
The paper went on to turn out to be a patent within the U.S. (however not in Europe, the place mathematical formulation should not patentable).
 Picture from patents.google.com, April 2023
Picture from patents.google.com, April 2023Stanford College owns the patent and has assigned it to Google. The patent is at the moment as a result of expire in 2027.
 Picture from patents.google.com, April 2023
Picture from patents.google.com, April 2023The Historical past Of How PageRank Developed
Throughout their time at Stanford within the late Nineteen Nineties, each Brin and Web page had been information retrieval strategies.
At the moment, utilizing hyperlinks to work out how “necessary” every web page was relative to a different was a revolutionary solution to order pages. It was computationally tough however under no circumstances unimaginable.
The concept shortly was Google, which at the moment was a minnow on the earth of search.
There was a lot institutional perception in Google’s strategy from some events that the enterprise initially launched its search engine with no capability to earn income.
And whereas Google (identified on the time as “BackRub”) was the search engine, PageRank was the algorithm it used to rank pages within the search engine outcomes pages (SERPs).
The Google Dance
One of many challenges of PageRank was that the maths, while easy, wanted to be iteratively processed. The calculation runs a number of instances, over each web page and each hyperlink on the Web. On the flip of the millennium, this math took a number of days to course of.
The Google SERPs moved up and down throughout that point. These adjustments had been usually erratic, as new PageRanks had been being calculated for each web page.
This was often called the “Google Dance,” and it notoriously stopped search engine marketing professionals of the day of their tracks each time Google began its month-to-month replace.
(The Google Dance later turned the identify of an annual social gathering that Google ran for search engine marketing specialists at its headquarters in Mountain View.)
Trusted Seeds
A later iteration of PageRank launched the concept of a “trusted seed” set to start out the algorithm slightly than giving each web page on the Web the identical preliminary worth.
Cheap Surfer
One other iteration of the mannequin launched the concept of a “cheap surfer.”
This mannequin means that the PageRank of a web page won’t be shared evenly with the pages it hyperlinks out to – however may weight the relative worth of every hyperlink based mostly on how doubtless a consumer is perhaps to click on on it.
The Retreat Of PageRank
Google’s algorithm was initially believed to be “unspam-able” internally because the significance of a web page was dictated not simply by its content material but additionally by a type of “voting system” generated by hyperlinks to the web page.
Google’s confidence didn’t final, nonetheless.
PageRank began to turn out to be problematic because the backlink trade grew. So Google withdrew it from public view, however continued to depend on it for its rating algorithms.
The PageRank Toolbar was withdrawn by 2016, and finally, all public entry to PageRank was curtailed. However by this time, Majestic (an search engine marketing software), particularly, had been in a position to correlate its personal calculations fairly effectively with PageRank.
Google spent a few years encouraging search engine marketing professionals away from manipulating hyperlinks via its “Google Guidelines” documentation and thru recommendation from its spam staff, headed up by Matt Cutts, till January 2017.
Google’s algorithms had been additionally altering throughout this time.
The corporate was relying much less on PageRank and, following the acquisition of MetaWeb and its proprietary Knowledge Graph (known as “Freebase” in 2014), Google began to index the world’s data in several methods.
Toolbar PageRank Vs. PageRank
Google was initially so pleased with its algorithm that it was blissful to publicly share the results of its calculation to anybody who wished to see it.
Essentially the most notable illustration was a toolbar extension for browsers like Firefox, which confirmed a rating between 0 and 10 for each web page on the Web.
In fact, PageRank has a a lot wider vary of scores, however 0-10 gave search engine marketing professionals and shoppers an immediate solution to assess the significance of any web page on the Web.
The PageRank Toolbar made the algorithm extraordinarily seen, which additionally got here with problems. Particularly, it meant that it was clear that hyperlinks had been the simplest solution to “sport” Google.
The extra hyperlinks (or, extra precisely, the higher the hyperlink), the higher a web page may rank in Google’s SERPs for any focused key phrase.
This meant {that a} secondary market was fashioned, shopping for and promoting hyperlinks valued on the PageRank of the URL the place the hyperlink was bought.
This downside was exacerbated when Yahoo launched a free software known as Yahoo Search Explorer, which allowed anybody the power to start out discovering hyperlinks into any given web page.
Later, two instruments – Moz and Majestic – constructed on the free choice by constructing their very own indexes on the Web and individually evaluating hyperlinks.
How PageRank Revolutionized Search
Different engines like google relied closely on analyzing the content material on every web page individually. These strategies had little to determine the distinction between an influential web page and one merely written with random (or manipulative) textual content.
This meant that the retrieval strategies of different engines like google had been extraordinarily simple for search engine marketing professionals to control.
Google’s PageRank algorithm, then, was revolutionary.
Mixed with a comparatively easy idea of “nGrams” to assist set up relevancy, Google discovered a successful system.
It quickly overtook the principle incumbents of the day, resembling AltaVista and Inktomi (which powered MSN, amongst others).
By working at a web page stage, Google additionally discovered a way more scalable resolution than the “listing” based mostly strategy adopted by Yahoo and later DMOZ – though DMOZ (additionally known as the Open Listing Venture) was in a position to present Google initially with an open-source listing of its personal.
How PageRank Works
The system for PageRank is available in quite a lot of types however might be defined in just a few sentences.
Initially, each web page on the web is given an estimated PageRank rating. This might be any quantity. Traditionally, PageRank was introduced to the general public as a rating between 0 and 10, however in apply, the estimates shouldn’t have to start out on this vary.
The PageRank for that web page is then divided by the variety of hyperlinks out of the web page, leading to a smaller fraction.
The PageRank is then distributed out to the linked pages – and the identical is finished for each different web page on the Web.
Then for the subsequent iteration of the algorithm, the brand new estimate for PageRank for every web page is the sum of all of the fractions of pages that hyperlink into every given web page.
The system additionally comprises a “damping issue,” which was described as the possibility that an individual browsing the online would possibly cease browsing altogether.
Earlier than every subsequent iteration of the algorithm begins, the proposed new PageRank is lowered by the damping issue.
This technique is repeated till the PageRank scores attain a settled equilibrium. The ensuing numbers had been then typically transposed right into a extra recognizable vary of 0 to 10 for comfort.
One solution to symbolize this mathematically is:
-
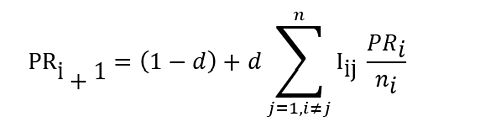 Picture from creator, April 2023
Picture from creator, April 2023
The place:
- PR = PageRank within the subsequent iteration of the algorithm.
- d = damping issue.
- j = the web page quantity on the Web (if each web page had a singular quantity).
- n=complete variety of pages on the Web.
- i = the iteration of the algorithm (initially set as 0).
The system can be expressed in Matrix kind.
Issues And Iterations To The Components
The system has some challenges.
If a web page doesn’t hyperlink out to every other web page, then the system won’t attain an equilibrium.
On this occasion, due to this fact, the PageRank can be distributed amongst each web page on the Web. On this method, even a web page with no incoming hyperlinks may get some PageRank – however it will not accumulate sufficient to be important.
One other much less documented problem is that newer pages, while probably extra necessary than older pages, may have a decrease PageRank. Because of this over time, outdated content material can have a disproportionately excessive PageRank.
The time a web page has been stay shouldn’t be factored into the algorithm.
How PageRank Flows Between Pages
If a web page begins with a price of 5 and has 10 hyperlinks out, then each web page it hyperlinks to is given 0.5 PageRank (much less the damping issue).
On this method, the PageRank flows across the Web between iterations.
As new pages come onto the Web, they begin with solely a tiny quantity of PageRank. However as different pages begin to hyperlink to those pages, their PageRank will increase over time.
Is PageRank Nonetheless Used?
Though public entry to PageRank was eliminated in 2016, it’s believed the rating remains to be obtainable to look engineers inside Google.
A leak of the components utilized by Yandex confirmed that PageRank remained as an element that it may use.
Google engineers have urged that the unique type of PageRank was changed with a brand new approximation that requires much less processing energy to calculate. While the system is much less necessary in how Google ranks pages, it stays a continuing for every net web page.
And no matter what different algorithms Google would possibly select to name upon, PageRank doubtless stays embedded in most of the search big’s methods to this present day.
Dixon explains how PageRank works in additional element on this video:
Unique Patents And Papers For Extra In-Depth Studying:
Extra assets:
Featured Picture: VectorMine/Shutterstock
[ad_2]


