[ad_1]
Should you’ve all the time been in awe of parents utilizing the Google Search Console API to do cool things, this text is an effective learn for you.
You should use BigQuery with the GSC bulk information export to get a few of the identical advantages with out requiring the assistance of a developer.
With BigQuery, you possibly can effectively analyze giant volumes of knowledge from the GSC bulk data export.
You gained’t have real-time information retrieval; that’s out there with the API in our situation however you can rely on daily data imports which implies that you’re working with up-to-date info.
By leveraging BigQuery and the GSC bulk information export, you possibly can entry complete search analytics information – that’s the half you hear everybody raving about on LinkedIn.
In keeping with Gus Pelogia, SEO product manager at Indeed:
“It’s such a sport changer and an awesome alternative to study SQL. We will lastly bypass GSC and exterior web optimization instruments limitations. I used to be shocked to see how easy it was to retrieve information.”
A Structured Strategy To Utilizing BigQuery And Google Search Console (GSC) Knowledge For Content material Efficiency Evaluation
The purpose of this text is to not offer you a protracted listing of queries or an enormous step-by-step blueprint of how one can conduct essentially the most intense audit of all time.
I purpose to make you’re feeling extra snug stepping into the groove of analyzing information with out the restrictions that include the Google Search Console interface. To do that, it’s worthwhile to take into account 5 steps:
- Establish use circumstances.
- Establish related metrics for every use case.
- Question the information.
- Create a looker studio report to assist stakeholders and groups perceive your evaluation.
- Automate reporting.
The problem we regularly face when getting began with BigQuery is that all of us wish to question the information instantly. However that’s not sufficient.
The true worth you possibly can convey is by having a structured method to your information evaluation.
1. Establish Use Instances
It’s usually advisable that you recognize your information earlier than you determine what you wish to analyze. Whereas that is true, on this case, will probably be limiting you.
We advocate you begin by figuring out the particular objective and targets for analyzing content material efficiency.
Use Case #1: Establish The Queries And Pages That Convey The Most Clicks
“I consider that each high-quality web optimization audit must also analyze the location’s visibility and efficiency in search. When you establish these areas, you’ll know what to concentrate on in your audit suggestions.”
Stated Olga Zarr in her “How to audit a site with Google Search Console” information.
To do this, you need the queries and the pages that convey essentially the most clicks.
Use Case #2: Calculating UQC
If you wish to spot weak areas or alternatives, calculating the Unique Query Count (UQC) per page affords beneficial insights.
You already know this since you use this kind of evaluation in web optimization instruments like Semrush, SE Rating, Dragon Metrics, or Serpstat (the latter has an awesome information on How to Use Google Search Console to Create Content Plans).
Nonetheless, it’s extremely helpful to recreate this with your individual Google Search Console information. You possibly can automate and replicate the method frequently.
There are advantages to this:
- It helps establish which pages are attracting a various vary of search queries and which of them could also be extra targeted on particular subjects.
- Pages with a excessive UQC could current alternatives for additional optimization or growth to capitalize on a wider vary of search queries.
- Analyzing the UQC per web page can even reveal which place bands (e.g., positions 1-3, 4-10, and so forth.) show extra variability by way of the variety of distinctive queries. This can assist prioritize optimization efforts.
- Understanding how UQC fluctuates all year long can inform content material planning and optimization methods to align with seasonal developments and capitalize on peak durations of search exercise.
- Evaluating UQC developments throughout totally different time durations lets you gauge the effectiveness of content material optimization efforts and establish areas for additional enchancment.
Use case #3: Assessing The Content material Threat
Jess Joyce, B2B & SaaS web optimization knowledgeable has a revenue generating content optimization framework she shares with shoppers.
One of many vital steps is discovering pages that noticed a decline in clicks and impressions quarter over quarter. She depends on Search Console information to take action.
Constructing this question can be nice however earlier than we soar into this, we have to assess the content material danger.
Should you calculate the proportion of complete clicks contributed by the highest 1% of pages on a web site based mostly on the variety of clicks every web page receives, you possibly can rapidly pinpoint in case you are within the hazard zone – which means if there are potential dangers related to over-reliance on a small subset of pages.
Right here’s why this issues:
- Over-reliance on a small subset of pages may be dangerous because it reduces the diversification of site visitors throughout the web site, making it weak to fluctuations or declines in site visitors to these particular pages.
- Assessing the hazard zone: A share worth over 40% signifies a excessive reliance on the highest 1% of pages for natural site visitors, suggesting a possible danger.
- This question offers beneficial perception into the distribution of natural site visitors throughout a web site.
2. Establish Related Metrics
Analyzing your content material permits you to discern which content material is efficient and which isn’t, empowering you to make data-informed choices.
Whether or not it’s increasing or discontinuing sure content material varieties, leveraging insights out of your information lets you tailor your content material technique to match your viewers’s preferences.
Metrics and evaluation in content material advertising and marketing present the important information for crafting content material that resonates together with your viewers.
Use Case #1: Establish The Queries And Pages That Convey The Most Clicks
For this use case, you want some fairly simple information.
Let’s listing all of it out right here:
- URLs and/or queries.
- Clicks.
- Impressions.
- Search kind: we solely need internet searches, not photos or different varieties.
- Over a selected time interval.
The following step is to find out which desk it is best to get this info from. Keep in mind, as we discussed previously, you might have:
- searchdata_site_impression: Accommodates efficiency information in your property aggregated by property.
- searchdata_url_impression: Accommodates efficiency information in your property aggregated by URL.
On this case, you want the efficiency information aggregated by URL, so this implies utilizing the searchdata_url_impression desk.
Use Case #2: Calculating UQC
For this use case, we have to listing what we’d like as nicely:
- URL: We wish to calculate UQC per web page.
- Question: We would like the queries related to every URL.
- Search Sort: We solely need internet searches, not photos or different varieties.
- We nonetheless want to choose a desk, on this case, you want the efficiency information aggregated by URL so this implies utilizing the searchdata_url_impression desk.
Use Case #3: Assessing The Content material Threat
To calculate the “clicks contribution of prime 1% pages by clicks,” you want the next metrics:
- URL: Used to calculate the clicks contribution.
- Clicks: The variety of clicks every URL has acquired.
- Search Sort: Signifies the kind of search, usually ‘WEB’ for internet searches.
- We nonetheless want to choose a desk, on this case, you want the efficiency information aggregated by URL so this implies utilizing the searchdata_url_impression desk. (Narrator voice: discover a pattern? We’re practising with one desk which lets you get very acquainted with it.)
3. Question The Knowledge
Use Case #1: Establish The Queries And Pages That Convey The Most Clicks
Let’s tie all of it collectively to create a question, we could?
You wish to see pages with essentially the most clicks and impressions. It is a easy code that you may get from Marco Giordano’s BigQuery handbook out there through his publication.
We’ve got barely modified it to go well with our wants and to make sure you maintain prices low.
Copy this question to get the pages with essentially the most clicks and impressions:
SELECT url, SUM(clicks) as total_clicks, SUM(impressions) as total_impressions FROM `pragm-ga4.searchconsole.searchdata_url_impression` WHERE search_type="WEB" and url NOT LIKE '%#%' AND data_date = "2024-02-13" GROUP BY url ORDER BY total_clicks DESC;
It depends on probably the most widespread SQL patterns. It lets you group by a variable, in our case, URLs. After which, you possibly can choose aggregated metrics you need.
In our case, we specified impressions and clicks so we might be summing up clicks and impressions (two columns).
Let’s break down the question Marco shared:
SELECT assertion
SELECT url, SUM(clicks) as total_clicks, SUM(impressions) as total_impressions: Specifies the columns to be retrieved within the consequence set.
- url: Represents the URL of the webpage.
- SUM(clicks) as total_clicks: Calculates the full variety of clicks for every URL and assigns it an alias total_clicks.
- SUM(impressions) as total_impressions: Calculates the full variety of impressions for every URL and assigns it an alias total_impressions.
FROM clause
- FROM table_name`pragm-ga4.searchconsole.searchdata_url_impression`: Specifies the desk from which to retrieve the information.
- table_name: Represents the identify of the desk containing the related information.
- Necessary to know: substitute our desk identify together with your desk identify.
WHERE clause
- WHERE search_type = ‘WEB’ and url NOT LIKE ‘%#%’: Filters the information based mostly on particular circumstances.
- search_type = ‘WEB’: Ensures that solely information associated to internet search outcomes is included.
- url NOT LIKE ‘%#%’: Excludes URLs containing “#” of their deal with, filtering out anchor hyperlinks inside pages.
- data_date = “2024-02-13”: This situation filters the information to solely embrace data for the date ‘2024-02-13’. It ensures that the evaluation focuses solely on information collected on this particular date, permitting for a extra granular examination of internet exercise for that day.
- (Narrator voice: we advocate you choose a date to maintain prices low.)
Necessary to know: We advocate you choose two days earlier than as we speak’s date to make sure that you might have information out there.
GROUP BY clause
- GROUP BY url: Teams the outcomes by the URL column.
- This teams the information in order that the SUM operate calculates complete clicks and impressions for every distinctive URL.
ORDER BY clause
- ORDER BY total_clicks DESC: Specifies the ordering of the consequence set based mostly on the total_clicks column in descending order.
- This arranges the URLs within the consequence set based mostly on the full variety of clicks, with the URL having the best variety of clicks showing first.
This question remains to be extra superior than most freshmen would create as a result of it not solely retrieves information from the fitting desk but additionally filters it based mostly on particular circumstances (eradicating anchor hyperlinks and search varieties that aren’t completely WEB).
After that, it calculates the full variety of clicks and impressions for every URL, teams the outcomes by URL, and orders them based mostly on the full variety of clicks in descending order.
That is why it is best to begin by your use case first, determining metrics second after which writing the question.
Copy this SQL to get the queries in GSC with essentially the most clicks and impressions:
SELECT question, SUM(clicks) as total_clicks, SUM(impressions) as total_impressions FROM `pragm-ga4.searchconsole.searchdata_url_impression` WHERE search_type="WEB" AND data_date = "2024-02-13" GROUP BY question ORDER BY total_clicks DESC;
This is similar question, however as a substitute of getting the URL right here, we’ll retrieve the question and mixture the information based mostly on this discipline. You possibly can see that within the GROUP BY question portion.
The issue with this question is that you’re prone to have a whole lot of “null” outcomes. These are anonymized queries. You possibly can take away these through the use of this question:
SELECT question, SUM(clicks) as total_clicks, SUM(impressions) as total_impressions FROM `pragm-ga4.searchconsole.searchdata_url_impression` WHERE search_type="WEB" AND is_anonymized_query = false AND data_date = "2024-02-13" GROUP BY Question ORDER BY total_clicks DESC;
Now, let’s go one step additional. I like how Iky Tai, SEO at GlobalShares went about it on LinkedIn. First, it’s worthwhile to outline what the question does: you possibly can see the high-performing URLs by clicks for a specific date vary.
The SQL question has to retrieve the information from the desired desk, filter it based mostly on a date vary, not a selected date, calculate the full variety of impressions and clicks for every URL, group the outcomes by URL, and organize them based mostly on the full variety of clicks in descending order.
Now that that is achieved, we will construct the SQL question:
SELECT url, SUM(impressions) AS impressions, SUM(clicks) AS clicks FROM `pragm-ga4.searchconsole.searchdata_url_impression` WHERE data_date BETWEEN DATE_SUB(CURRENT_DATE(), INTERVAL 3 DAY) AND DATE_SUB(CURRENT_DATE(), INTERVAL 1 DAY) GROUP BY url ORDER BY clicks DESC;
Earlier than you copy-paste your strategy to glory, take the time to grasp how that is constructed:
SELECT assertion
- SELECT url, SUM(impressions) AS impressions, SUM(clicks) AS clicks: Specifies the columns to be retrieved within the consequence set.
- url: Represents the URL of the webpage.
- SUM(impressions) AS impressions: Calculates the full variety of impressions for every URL.
- SUM(clicks) AS clicks: Calculates the full variety of clicks for every URL.
FROM clause
- FROM searchconsole.searchdata_url_impression: Specifies the desk from which to retrieve the information.
- (Narrator voice: You’ll have to substitute the identify of your desk.)
- searchconsole.searchdata_url_impression: Represents the dataset and desk containing the search information for particular person URLs.
WHERE clause
- WHERE data_date BETWEEN DATE_SUB(CURRENT_DATE(), INTERVAL 3 DAY) AND DATE_SUB(CURRENT_DATE(), INTERVAL 1 DAY): Filters the information based mostly on the date vary.
- data_date: Represents the date when the search information was recorded.
- BETWEEN: Specifies the date vary from three days in the past (INTERVAL 3 DAY) to yesterday (INTERVAL 1 DAY).
- DATE_SUB(CURRENT_DATE(), INTERVAL 3 DAY): Calculates the date three days in the past from the present date.
- DATE_SUB(CURRENT_DATE(), INTERVAL 1 DAY): Calculates yesterday’s date from the present date.
Necessary to know: As we mentioned beforehand, you might not have information out there for the earlier two days. Which means that you would change that interval to say 5 and three days as a substitute of three and at some point.
GROUP BY clause
GROUP BY url: Teams the outcomes by the URL column.
- This teams the information in order that the SUM operate calculates impressions and clicks for every distinctive URL.
ORDER BY clause
ORDER BY clicks DESC: Specifies the ordering of the consequence set based mostly on the clicks column in descending order.
- This arranges the URLs within the consequence set based mostly on the full variety of clicks, with the URL having the best variety of clicks showing first.
Necessary notice: when first getting began, I encourage you to make use of an LLM like Gemini or ChatGPT to assist break down queries into chunks you possibly can perceive.
Use Case #2: Calculating UQC
Right here is one other helpful Marco’s handbook that now we have modified as a way to get you seven days of knowledge (per week’s value):
SELECT url, COUNT(DISTINCT(question)) as unique_query_count FROM `pragm-ga4.searchconsole.searchdata_url_impression` WHERE search_type="WEB" and url NOT LIKE '%#%' AND data_date BETWEEN DATE_SUB(CURRENT_DATE(), INTERVAL 10 DAY) AND DATE_SUB(CURRENT_DATE(), INTERVAL 3 DAY) GROUP BY url ORDER BY unique_query_count DESC;
This time, we is not going to break down the question.
This question calculates the Distinctive Question Rely (UQC) per web page by counting the distinct queries related to every URL, excluding URLs containing ‘#’ and filtering for internet searches.
It does that for an interval of seven days whereas making an allowance for information might not be out there for the 2 earlier days.
The outcomes are then sorted based mostly on the rely of distinctive queries in descending order, offering insights into which pages entice a various vary of search queries.
Use Case #3: Assessing The Content material Threat
This question calculates the proportion of complete clicks accounted for by the highest 1% of URLs by way of clicks. It is a way more superior question than the earlier ones. It’s taken straight from Marco’s Playbook:
WITH PageClicksRanked AS ( SELECT url, SUM(clicks) AS total_clicks, PERCENT_RANK() OVER (ORDER BY SUM(clicks) DESC) AS percent_rank FROM `pragm-ga4.searchconsole.searchdata_url_impression` WHERE search_type="WEB" AND url NOT LIKE '%#%' GROUP BY url ) SELECT ROUND(SUM(CASE WHEN percent_rank <= 0.01 THEN total_clicks ELSE 0 END) / SUM(total_clicks) * 100, 2) AS percentage_of_clicks FROM PageClicksRanked;
This SQL question is extra advanced as a result of it incorporates superior methods like window features, conditional aggregation, and customary desk expressions.
Let’s break it down:
Frequent Desk Expression (CTE) – PageClicksRanked
- This a part of the question creates a brief consequence set named PageClicksRanked.
- It calculates the full variety of clicks for every URL and assigns a percentile rank to every URL based mostly on the full variety of clicks. The percentile rank is calculated utilizing the PERCENT_RANK() window operate, which assigns a relative rank to every row inside a partition of the consequence set.
- Columns chosen:
- url: The URL from which the clicks originated.
- SUM(clicks) AS total_clicks: The whole variety of clicks for every URL.
- PERCENT_RANK() OVER (ORDER BY SUM(clicks) DESC) AS percent_rank: Calculates the percentile rank for every URL based mostly on the full variety of clicks, ordered in descending order.
Situations
- search_type = ‘WEB’: Filters the information to incorporate solely internet search outcomes.
- AND url NOT LIKE ‘%#%’: Excludes URLs containing “#” from the consequence set.
Grouping
- GROUP BY url: Teams the information by URL to calculate the full clicks for every URL.
Predominant Question
- This a part of the question calculates the proportion of complete clicks accounted for by the highest 1% of URLs by way of clicks.
- It sums up the full clicks for URLs whose percentile rank is lower than or equal to 0.01 (prime 1%) and divides it by the full sum of clicks throughout all URLs. Then, it multiplies the consequence by 100 to get the proportion.
Columns chosen
- ROUND(SUM(CASE WHEN percent_rank <= 0.01 THEN total_clicks ELSE 0 END) / SUM(total_clicks) * 100, 2) AS percentage_of_clicks: Calculates the proportion of clicks accounted for by the highest 1% of URLs. The CASE assertion filters out the URLs with a percentile rank lower than or equal to 0.01, after which it sums up the full clicks for these URLs. Lastly, it divides this sum by the full sum of clicks throughout all URLs and multiplies it by 100 to get the proportion. The ROUND operate is used to around the consequence to 2 decimal locations.
Supply
- FROM PageClicksRanked: Makes use of the PageClicksRanked CTE as the information supply for calculations.
(Narrator voice: this is the reason we don’t share extra advanced queries instantly. Writing advanced queries instantly requires information, apply, and understanding of the underlying information and enterprise necessities.)
To be able to write such queries, you want:
- A stable understanding of SQL syntax: SELECT statements, GROUP BY, mixture features, subqueries and window features to start out.
- A deep understanding of the database schema which is why we took the time to go through them in another article.
- Observe! Writing and optimizing SQL queries does the trick. So does engaged on datasets and fixing analytical issues! Observe means taking an iterative method to experiment, check and refine queries.
- Having a superb cookbook: Setting apart good queries you possibly can tweak and depend on.
- Drawback-solving abilities: To seek out the fitting method, you might have to have the ability to break down advanced analytical duties into manageable steps. That’s why we began with the five-step framework.
- A efficiency mindset: You wish to enhance question efficiency, particularly for advanced queries working on giant datasets. Should you don’t, you would find yourself spending some huge cash in BigQuery.
4. Create Looker Studio Dashboards
As soon as that is achieved, you should utilize Looker Studio to construct dashboards and visualizations that showcase your content material efficiency metrics.
You possibly can customise these dashboards to current information in a significant approach for various stakeholders and groups. This implies you aren’t the one one accessing the knowledge.
We’ll dive into this portion of the framework in one other article.
Nonetheless, if you wish to get began with a Looker Studio dashboard utilizing BigQuery information, Emad Sharaki shared his awesome dashboard. We advocate you give it a attempt.
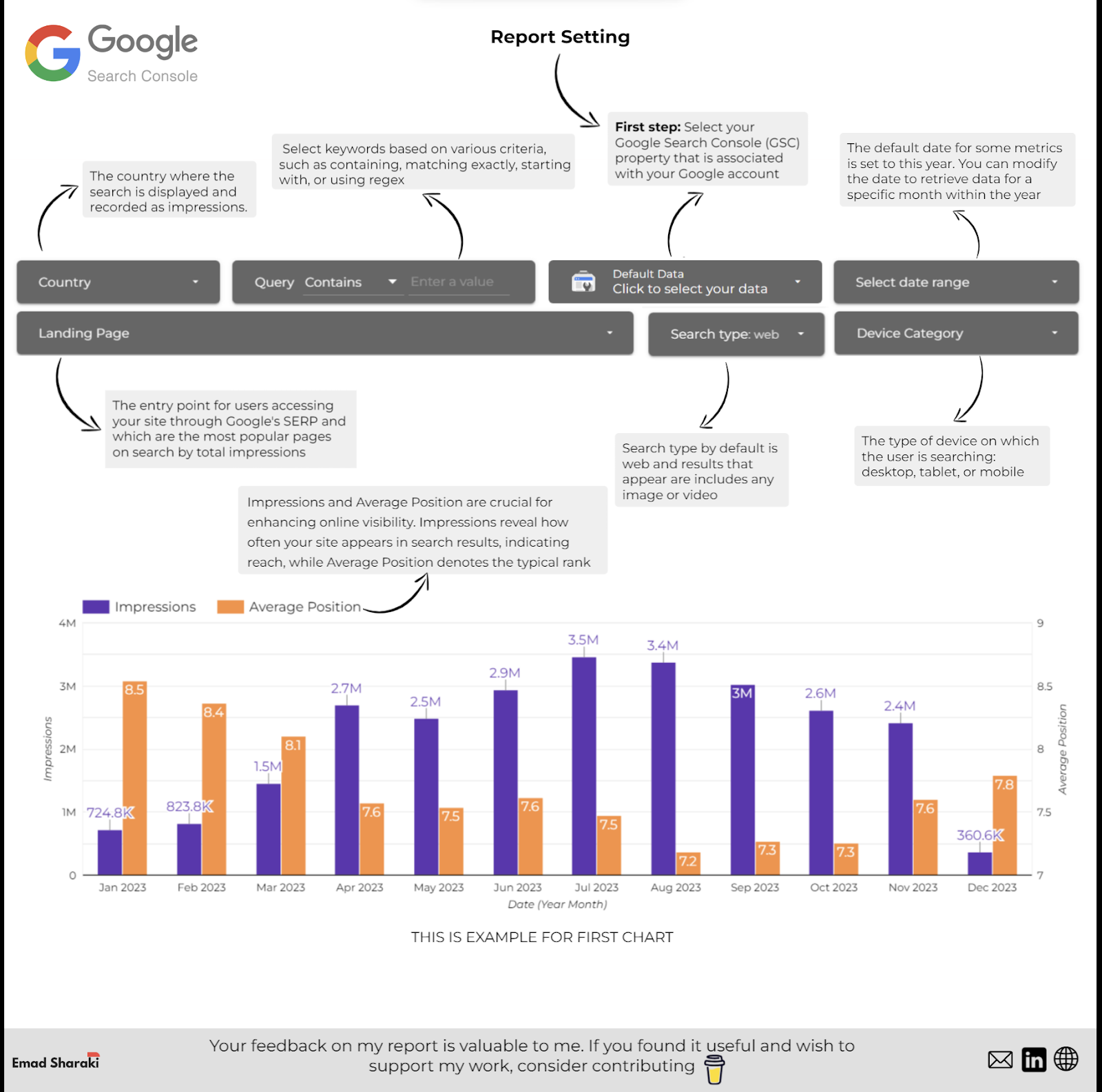 Picture from Emad Sharaki, February 2024
Picture from Emad Sharaki, February 20245. Automate Reporting
After you have achieved all this, you possibly can arrange scheduled queries in BigQuery to routinely fetch GSC information current within the tables at common intervals.
This implies you possibly can automate the era and distribution of reviews inside your organization.
You can check out the official documentation for this portion for now. We’ll cowl this at a later date in one other devoted article.
The one tip we’ll share right here is that it is best to schedule queries after the everyday export window to make sure you’re querying the newest out there information.
To be able to monitor the information freshness, it is best to monitor export completion instances in BigQuery’s export log.
You should use the reporting automation to allow different groups relating to content material creation and optimization. Gianna Brachetti-Truskawa, web optimization PM and strategist, helps editorial groups by integrating reviews instantly into the CMS.
This implies editors can filter current articles by efficiency and prioritize their optimization efforts accordingly. One other automation reporting factor to contemplate is to combine with Jira to attach your efficiency to a dashboard with customized guidelines.
Which means that articles may be pulled to the highest of the backlog and that seasonal subjects may be added to the backlog in a well timed method to create momentum.
Going Additional
Clearly, you have to extra use circumstances and a deeper understanding of the kind of content material audit you wish to conduct.
Nonetheless, the framework we shared on this article is an effective way to make sure issues keep structured. If you wish to take it additional, Lazarina Stoy, web optimization information knowledgeable, has just a few suggestions for you:
“When doing content material efficiency evaluation, it’s vital to grasp that not all content material is created equal. Make the most of SQL Case/When statements to create subsets of the content material based mostly on web page kind (firm web page, weblog put up, case examine, and so forth.), content material construction patterns (idea explainer, information merchandise, tutorial, information, and so forth), title patterns, goal intent, goal audiences, content material clusters, and every other kind of classification that’s distinctive to your content material.
That approach you possibly can monitor and troubleshoot in case you detect patterns which can be underperforming, in addition to amplify the efforts which can be paying off, at any time when such are detected.”
Should you create queries based mostly on these concerns, share them with us so we will add them to the cookbook of queries one can use for content material efficiency evaluation!
Conclusion
By following this structured method, you possibly can successfully leverage BigQuery and GSC information to research and optimize your content material efficiency whereas automating reporting to maintain stakeholders knowledgeable.
Keep in mind, accumulating everybody else’s queries is not going to make you an in a single day BigQuery professional. Your worth lies in determining use circumstances.
After that, you possibly can determine the metrics you want and tweak the queries others created or write your individual. After you have that within the bag, it’s time to be an expert by permitting others to make use of the dashboard you created to visualise your findings.
Your peace of thoughts will come when you automate a few of these actions and develop your abilities and queries much more!
Extra sources:
Featured Picture: Suvit Topaiboon/Shutterstock
[ad_2]
Source link